Periodontitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease, is a widespread oral health issue that can have serious consequences if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the symptoms and causes, available treatments, and even explore periodontisis at home treatment options. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of periodontitis and how to manage it effectively.
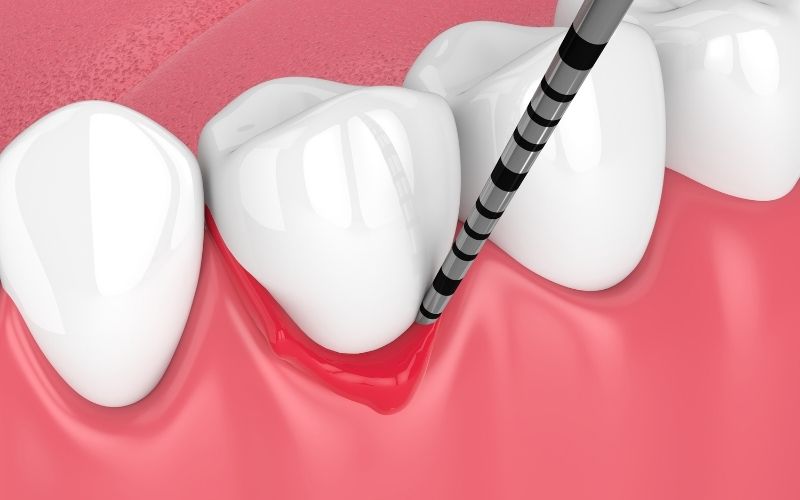
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone that supports your teeth. It is typically caused by poor oral hygiene habits that allow bacteria to build up on the teeth and eventually spread to the gum tissue. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
The condition is also associated with certain diseases like diabetes, making its management a crucial part of overall health care. It’s important to note that periodontitis is not a sudden occurrence, but rather a progression from gingivitis, the milder form of gum disease.
Related Post: Periodontal Disease Guide.
Periodontitis vs. Gingivitis
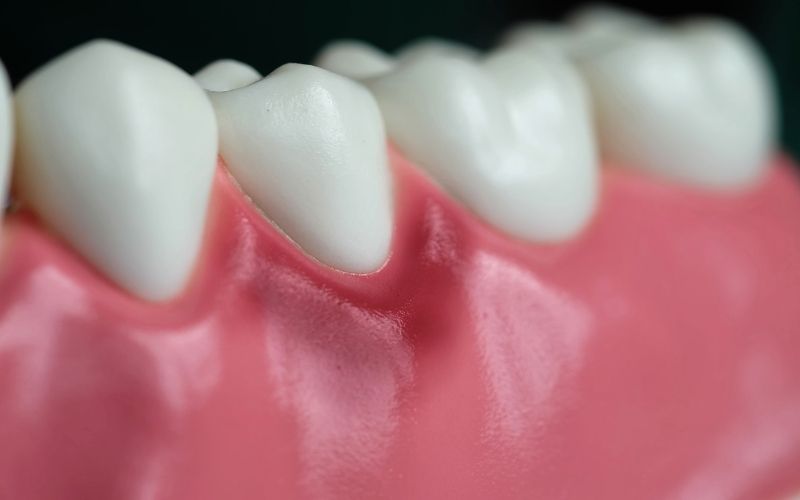
First of all they are both periodontal diesease and gingivitis is the first stage of periodontal. It’s important to note that gingivitis is a warning sign for potential development of periodontitis, and it’s crucial to address it early on to prevent further damage.However, there are key differences between the two conditions:
- Gingivitis affects only the gum tissue and is reversible with proper oral hygiene and dental cleanings.
- Periodontitis affects both the gum tissue and bone supporting the teeth and can lead to irreversible damage if not treated promptly
- Gingivitis is characterized by inflamed and bleeding gums, while periodontitis can also cause receding gums, loose teeth, and even tooth loss.
- Gingivitis does not cause bone loss, while periodontitis can lead to severe bone loss and even affect the structure of the jawbone.
- While gingivitis is usually painless, periodontitis can cause discomfort, pain, and sensitivity in the affected area.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Some common symptoms to look out for include:
- Persistent bad breath
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a dentist as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Causes of Periodontitis
The main cause of periodontitis is the buildup of plaque on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film made up of bacteria, mucus, and food particles that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not regularly removed through proper oral hygiene practices, it hardens into tartar or calculus, which can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
Other risk factors for periodontitis include:
- Poor oral hygiene habits such as inadequate brushing and flossing
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Genetic predisposition
- Certain medications that can cause dry mouth or affect gum health
- Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or menopause
Periodontitis Treatment
The main goal of treatment for periodontitis is to control the infection and prevent further damage to the gums and bone.
Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include:
- Professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) to remove bacteria from pockets between the teeth and gums
- Antibiotics or antimicrobial mouthwashes to kill bacteria.
- Surgery, such as gum grafts or bone grafts, for severe cases.
Periodontitis at Home Treatment
While professional treatment is necessary for managing periodontitis, there are steps you can take at home to support the healing process. These include:
- Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Flossing daily to remove plaque and debris from between teeth
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash
- Quitting smoking or tobacco use
- Eating a balanced diet and avoiding sugary or sticky foods
- Managing any underlying health conditions, such as diabetes.
Related Posts: How to Stop Bleeding Gums?
Last Words from The More Clinics
At The More Clinics, we’re dedicated to helping you achieve and maintain a healthy smile. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into periodontitis and its management. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for ensuring the best outcomes. If you have further questions or require professional assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Your oral health is our priority.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION!
Let’s Start Planning Your Treatment %100 Guarantee Results.

Written by The More Editorial Team and Medically Reviewed by Mehmet Can Kılınçaslan who specialized on Periodontology and Implantology