All You Need to Know About Diabetes
One health concern that affects millions worldwide is diabetes mellitus. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need about diabetes, covering various aspects such as types, prediabetes, symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, treatment, diet, exercise, diagnosis, prevention, and its occurrence in pregnancy and children. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of diabetes and how to manage it effectively.
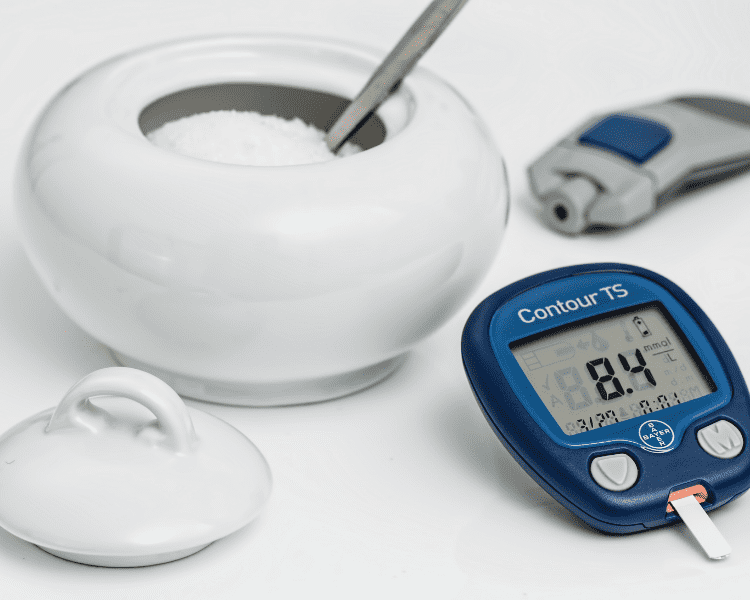
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition caused by either the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or to make effective use of it. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels in your body. Diabetes can lead to serious health complications if left untreated, such as nerve damage, heart disease, stroke and kidney failure.
Facts about Diabetes
According to the World Health Organization, 425 million adults (aged over 18) have diabetes and 1.6 million people die from it each year. It is the 7th leading cause of death worldwide and a major cause of blindness, lower limb amputation and kidney failure. Diabetes doubles the risk of cardiovascular disease, and about 75% of deaths in people with diabetes are due to coronary artery disease. Approximately 37.3 million people in the United States have diabetes, which is about 11% of the population.
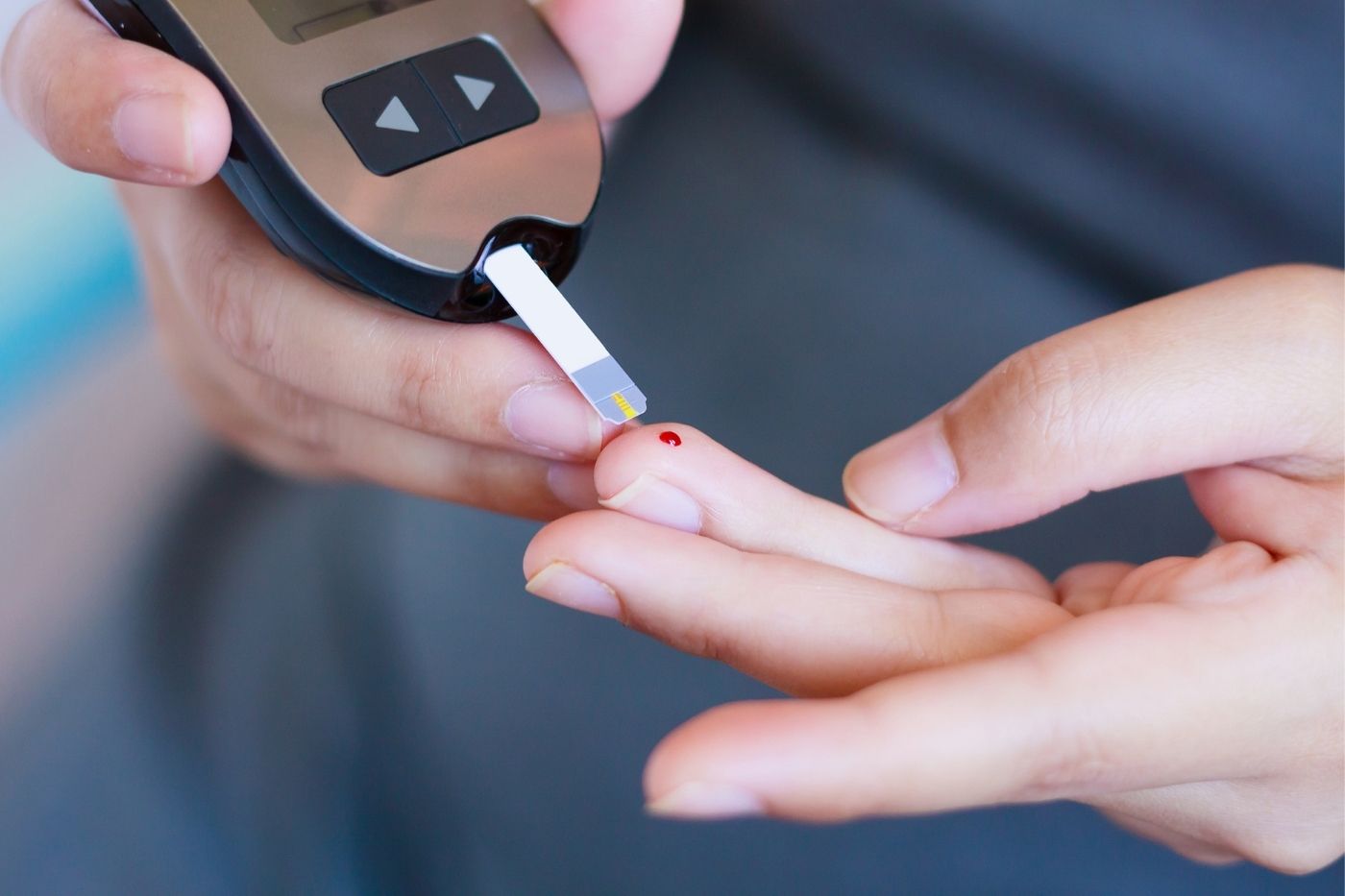

Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetes isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition; there are different types, each with its own characteristics:
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.- It accounts for about 10% of all cases of diabetes.
- Patients with type 1 diabetes need to take daily insulin injections or use an insulin pump to survive.
- It usually develops in childhood or adolescence.
Type 2 Diabetes
- It is usually diagnosed in adulthood and occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the available insulin (insulin resistance). – It is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases.
- People with type 2 diabetes typically must take medication and/or manage their diet to control their blood sugar levels.
- It is often associated with lifestyle factors like obesity and lack of physical activity.It can often be managed through lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and exercise.
Gestational Diabetes
- Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.- It is caused by hormones produced during pregnancy that temporarily interfere with the body’s ability to produce insulin.
- Women who have had gestational diabetes are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Type 1.5 Diabetes
- Also known as Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA), type 1.5 diabetes is a hybrid of type 1 and 2.- It is an autoimmune form of diabetes that progresses more slowly than type 1 diabetes, but faster than type 2.
- It has features of both types, including the need for insulin therapy like type 1 but also affected by lifestyle factors similar to type 2.
- It tends to develop later in adulthood and is often misdiagnosed as type 2 initially.
Prediabetes: A Warning Sign
Prediabetes is a condition that precedes type 2 diabetes. Understanding it can help prevent diabetes:
- Prediabetes occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes.
- It is estimated that 84 million American adults have prediabetes and 90% of them don’t know it.- Prediabetes can often be reversed with lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity levels and improving eating habits.

Symptoms and Causes of Diabetes
Common Symptoms of diabetes
Identifying diabetes early is vital for effective management. Look out for these common symptoms:-
- Excessive thirst
- Excessive hunger
- Extreme fatigue or lack of energy
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Pain or numbness in the hands, feet or legs
Causes of Diatebes
Diabetes is caused by an excess of glucose in the bloodstream, regardless of the type. However, the underlying reasons for elevated blood glucose levels vary depending on the specific type of diabetes. Diabetes can be triggered by a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
- Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition that occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies and attacks the insulin-producing cells located in the pancreas, leading to their destruction.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity. – It can also be triggered by genetics or a combination of both- Other less common causes of diabetes include certain medications, pancreatic disease, endocrine disorders and genetic syndromes.
- Type 1.5 diabetes is believed to be triggered by an autoimmune response, similar to type 1 diabetes, but the process occurs more slowly.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
It is important to be aware of the factors that can increase your risk of developing diabetes:-
Type 1:
- Family history of type 1 diabetes
- Exposure to certain viruses
Type 2:
- Being overweight or obese
- Being aged 45 or older
- Having a family history of the condition
- Having a sedentary lifestyle
- Having prediabetes
- Having high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or high triglyceride levels
Gestational diabetes:
- Age 25 or more
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Having previously had gestational diabetes
- Being overweight before pregnancy.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Complications of Diabetes
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to severe complications. Short-term (acute) complications include:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – a life-threatening condition caused by very high levels of blood sugar.
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) is a life-threatening condition caused by extremely high blood sugar levels. It occurs when blood sugar levels remain persistently elevated (over 600 milligrams per deciliter or mg/dL) for an extended period, resulting in severe dehydration and confusion. Immediate medical attention is imperative for its management and treatment.
- Sever low blood sugar (hypoglycemia): Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood sugar level falls below a healthy range.
Long-term (chronic) complications include:
- Cardiovascular diseases such as:
-heart attack -stroke – coronary artery diseases
- Kidney damage (neuropathy) or failure
- Eye damage, including diabetic retinopathy (damage to the retina and can lead to blindness).
- Nerve damage or neuropathy, which can cause:
-pain and numbness in your hands and feet
- Foot problems such as:
-ulcers -poor circulation.
- Sexual dysfunction resulting from nerve and blood vessel damage, such as erectile dysfunction or vaginal dryness, can significantly impact intimate experiences.
- Skin conditions such as:
-bacterial and fungal infections -itching.
- Cognitive impairment including dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and depression.
- Gum diesase
- Hearing loss
How Diabetes Diagnosed?
Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests, which measure the level of glucose in your bloodstream. Fasting blood glucose levels higher than 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) indicate diabetes.
Other tests include the glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, which measures the average amount of glucose in your blood over the past two to three months.A1C levels higher than 6.5% indicate diabetes.
If the results of these tests are inconclusive, your doctor may recommend an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). This involves drinking a high-sugar drink and measuring your blood sugar at specific intervals afterwards to determine how well your body processes glucose.
Treatment and Management
Diabetes is managed by doctors through the use of various medications. These treatments can be administered orally or through injections, offering different options for patients.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is most often managed through lifestyle and diet changes, including exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
Medications for type 2 diabetes include:
- Metformin – This drug helps regulate the amount of glucose produced in the body.
- Sulfonylureas – These drugs stimulate insulin production –
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) – This group of medications makes cells more sensitive to insulin
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor- Reduces blood glucose by increasing the amount of insulin your body releases
- GLP-1 agonists – These drugs help reduce appetite and stimulate insulin.
Type 1 and 1.5 diabetes
Type 1 and type 1.5 diabetes are managed with the use of insulin injections. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells so it can be used for energy. The most commonly used types of insulin include:
Rapid-acting insulin – This type of insulin starts to work within minutes and only lasts a few hours.
Short-acting insulin – This type of insulin takes a little longer to begin working, but lasts for around 8 hours
Intermediate-acting insulin – This type of insulin starts to work within 2 to 4 hours and lasts for up to 24 hours.
Long-acting insulin – This type of insulin starts to work in 1 or 2 hours and lasts for up to36 hours.
Diet and Diabetes
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in the management and prevention of diabetes. Unhealthy eating patterns, such as consuming high amounts of processed food, saturated fats, and sugary drinks, can lead to obesity, a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
On the other hand, a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight and stabilize blood glucose levels.
For individuals already living with diabetes, dietary choices are even more critical. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, making it harder to control diabetes. Instead, focusing on low-glycemic, nutrient-dense foods can help control blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Furthermore, portion control and meal planning can assist in maintaining steady blood glucose levels and managing body weight.
Type 2 diabetes and Diet
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are more likely to benefit from a structured lifestyle approach, which includes physical activity and dietary modifications. Research has found that following a Mediterranean-style diet can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or delay its progression.
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes eating minimally processed foods, plenty of fruits and vegetables, fish, whole grains, monounsaturated fats, such as extra virgin olive oil, and healthy proteins.
It also encourages limiting red meat and processed meats, avoiding added sugars and refined starches like white bread and pasta. Studies have found that following a Mediterranean diet can help improve blood sugar levels, delay progression of type 2 diabetes, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Moreover, this diet has been found to be beneficial for weight management, as it encourages portion control and moderate consumption of healthy fats. Furthermore, following a Mediterranean diet can help individuals with type 2 diabetes reduce their risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications related to the condition.
Type 1 / Type 1,5 Diabetes and Diet
For individuals with type 1 and type 1.5 diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is essential for managing the condition. Blood sugar testing can help track how food affects glucose levels throughout the day and inform insulin dosage decisions.
It’s important to check blood sugar levels before meals, two hours after meals, before and after physical activity, at bedtime, whenfeeling ill, and any other time recommended by a healthcare professional. Meal planning is also critical for type 1 and type 1.5 diabetics, as carbohydrates and sugar intake need to be balanced with insulin doses. This is known as carb counting, and can help individuals control blood glucose levels more effectively.
For instance, eating a small snack before physical activity can prevent low blood sugar during exercise. Additionally, including dietary supplements likevitamin B12 or omega-3 fatty acids may also help support blood sugar management.
Diabetes and Pregnancy
Women who never had diabetes can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, which occurs when the body is not able to produce enough insulin to manage glucose levels. This type of diabetes typically goes away after giving birth, however it puts an individual at a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later on.
Women with pre-existing diabetes also need to take extra care during pregnancy. It’s important to discussdiabetes management with a healthcare provider before and during pregnancy in order to reduce the risk of complications.
Pregnant women should eat balanced meals and snacks, monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, get regular physical activity, maintain a healthy weight, and take medications as prescribed. In some cases, insulin may be required for managing diabetes during the pregnancy.
Diabetes in Children
Children can develop either type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Parents and caregivers should be aware of the signs and symptoms of diabetes in children, which include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing wounds.
Diabetes can be difficult to manage in children as they may not be able to accurately express their symptoms or understand the importance of managing the condition.
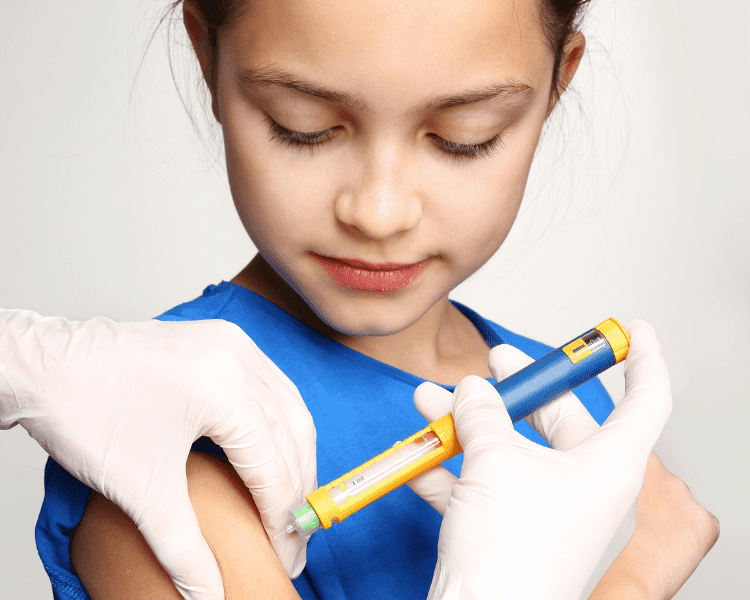
For children with type 1 diabetes, insulin injections or a pump are needed to maintain blood glucose levels. Additionally, it is important for them to eat balanced meals, monitor their blood sugar regularly throughout the day, and be active.
For children with type 2 diabetes, physical activity and dietary modifications may help manage the condition without medication. Eating smaller portions of healthy foods like fruitsand vegetables and avoiding snacks highin sugar or saturated fat can help control blood glucose levels.
Exercise and Diabetes
Exercise can play a key role in managing diabetes. Physical activity helps the body use insulin more effectively, reduces inflammation, and improves cardiovascular health.
Regular exercise is one of the most important lifestyle modifications for people living with all types of diabetes.
It’s recommended that adults with diabetes get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activities per week or 75minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week.
Examples of physical activities include walking, running, biking, swimming, and yoga.
In addition to the benefits for diabetes management, exercise can also help reduce stress and improve mood. It’s important to speak with a healthcare professional before beginning any type of exercise program as they can provide personalized advice and guidance on
Diabetes Prevention
Type 1 or type 1.5 diabetes cannot be prevented as they are caused by the immune system. Similarly, type 2 diabetes, when is influenced by genetic factors and age, is beyond your control.
However, people with a family history of type 2 diabetes may be able to reduce their risk of developing it through lifestyle modifications.
Lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes include:
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Adopting a balanced diet consisting of whole grains, lean proteins, fruits and vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Limiting the intake of processed foods and drinks high in sugar.
- Reducing sedentary behaviors such as prolonged sitting.
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Ceasing smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Regularly visiting a healthcare professional for preventive check-ups and guidance.
Last Words from the More Clinics
Diabetes is effecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it is possible to control the condition and lead an active life. It’s important to work closely with healthcare practitioners for diagnosis, treatment, advice, and support. Making lifestyle modifications such as following a balanced diet, regularly exercising, maintaining a healthy weight, and monitoring blood sugar levels can help manage diabetes more effectively.
At More Clinics, our team of healthcare professionals is committed to helping individuals living with diabetes achieve their best outcomes and live healthier lives. So if you have questions or concerns about managing your diabetes, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us!
GET A FREE CONSULTATION!
Let’s Start Planning Your Treatment %100 Guarantee Results.