Surgical Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of blood sugar, insulin resistance, and a decreased ability to produce insulin. While there are various treatment options available for type 2 diabetes, including medication and lifestyle changes, diabetes surgery is becoming increasingly popular. In this article, we will explore the surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes and its effectiveness in managing the condition.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body is unable to properly use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This leads to high levels of glucose in the blood, which can cause a range of health problems, including heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney damage.

Traditional Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes
The traditional treatment options for type 2 diabetes include medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring blood sugar levels. Medications such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents are commonly prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also help improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
While these treatment options can be effective in managing type 2 diabetes, they may not be suitable for everyone. Some people may not respond well to medication, and lifestyle changes can be difficult to maintain in the long term. This is where surgical treatment comes in.
Surgical Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Surgical treatment for type 2 diabetes involves procedures that aim to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
What is Diabetes Surgery?
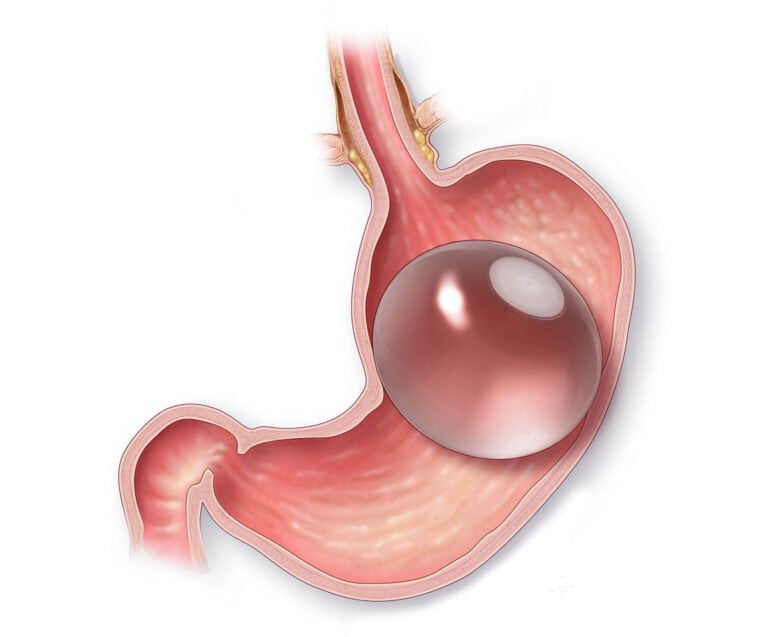
The diabetes surgery also known as metabolic surgery involves altering the digestive system to promote weight loss and improve metabolic function.
Diabetes surgery is typically performed on individuals with Type 2 diabetes who are obese, have high blood sugar levels, and have not achieved desired glucose levels despite medication and insulin use. This surgery is minimally invasive, involving the removal of 50% of the stomach and a change in the position of the small intestine. This alteration prompts the pancreas to secrete insulin more effectively, leading to the complete disappearance of Type 2 diabetes. Additionally, individuals also experience weight loss following the surgery. The advantages of this procedure include minimal pain compared to open surgeries, no lung-related complications, and a quick recovery with no visible scars.
Aim of the Diabetes Surgery
The objective of diabetes surgery is to eliminate insulin resistance in the body, resulting in an increase in hormone levels. For Type 1 diabetes, insulin is the preferred treatment, while for Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, medication, and surgery may be necessary if organ damage has occurred.
Effectiveness of Surgical Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Studies have shown that surgical treatment for type 2 diabetes can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels, weight loss, and overall health. In fact, some studies have reported that up to 80% of patients who undergo metabolic surgery experience remission of their type 2 diabetes.
One study published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared the effectiveness of gastric bypass surgery and intensive medical therapy in managing type 2 diabetes. The results showed that 42% of patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery achieved remission of their diabetes, compared to only 12% of patients who received medical therapy.
Is it effective for Type 1 Diabetes?
No its not. Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune disorder that destroys the body’s ability to produce insulin. Therefore, surgical treatment aimed at improving insulin sensitivity would not be effective in managing type 1 diabetes.
Who is a Good Candidate for Surgical Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes?
Not everyone with type 2 diabetes is a good candidate for surgical treatment. Generally, candidates for metabolic surgery should meet the following criteria:
Eligibility for Diabetes Surgery
Patients who are considered for diabetes surgery generally exhibit the following characteristics:
- They have been dealing with worsening Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for over a year, with or without other risk factors and complications, be they microvascular or macrovascular.
- They have mild to moderate complications associated with diabetes such as nephropathy, retinopathy, or nonhealing ulcers.
- There’s a strong family history of diabetes complications.
- Their glycemic control remains poor despite having optimum medical treatment.
- They are between the ages of 20 and 70.
- Their weight has been stable for the last 3 months (with less than 3% variation).
- They have a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2.
- There’s fluctuating glycemic control with comorbidity, even with good HbA1c levels.
- They have a stimulated C-peptide level greater than 1 ng/mL.
However, some patients are not considered suitable for diabetes surgery, including:
- Those diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes mellitus, latent autoimmune diabetes of adult (LADA), or maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), determined by estimations of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibody/islet cell antibody (ICA)/insulin auto-antibody (IAA2) and clinical course evaluation by endocrinologists.
- Those with undetectable fasting C-peptide and stimulated C-peptide less than 1 ng/mL.
- Those with positive urine ketone tests.
- Pregnant women.
- Those with severe coexisting conditions including hepatic, pulmonary, renal diseases (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 30 mL/min), cardiovascular, neurological, and psychiatric diseases.
Potential Benefits
The potential benefits of metabolic surgery for Type 2 Diabetes patients include:
Weight Loss: While weight loss is not the primary goal of metabolic surgery, it is often a beneficial side effect. This can lead to improved health outcomes across the board, including lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease.
Improved Quality of Life: With better management of blood sugar levels and weight loss, patients often report an improved quality of life after metabolic surgery. This includes greater energy levels, better mobility, and improved overall wellbeing.

Improved Blood Sugar Control: Many patients experience significant improvements in their blood sugar levels following metabolic surgery. This can lead to less reliance on medication, and in some cases, complete remission of the disease.
Reduced Risk of Future Complications: By improving blood sugar control and achieving weight loss, metabolic surgery can help to reduce the risk of future health complications associated with type 2 diabetes. These may include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and eye problems.
Lower Mortality Rate: Several studies have shown that metabolic surgery can lead to a significant reduction in mortality rate among patients with type 2 diabetes.
Risks and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with metabolic surgery for type 2 diabetes. These may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Dumping syndrome (a condition where food moves too quickly through the digestive system)
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Gallstones
- Complications related to anesthesia
It is important to discuss these risks with your doctor and weigh them against the potential benefits of the surgery.
Recovery and Tips for a Smooth Recovery
The recovery process for metabolic surgery shares several similarities with that of bariatric surgery.
You can also read Gastric Sleeve Recovery Guide.
Here are some tips to recovery:
- Follow postoperative guidelines provided by your healthcare team, including dietary restrictions and physical activity recommendations.
- Take prescribed medications as directed to minimize pain and discomfort.
- Stay hydrated and follow a gradual progression of food intake to allow your stomach to heal properly.
- Avoid strenuous activities for at least 6-8 weeks after surgery and gradually incorporate exercise into your daily routine.
- Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare team to monitor your progress and address any concerns or issues that may arise.
- Seek emotional support from friends, family, or a support group as you navigate this change in your life.
- Make long-term lifestyle changes to maintain the benefits of metabolic surgery, including healthy eating habits and regular physical activity.
Differences of Metabolic Surgery and Bariatric Surgery?
Metabolic surgery and bariatric surgery are both surgical treatments for type 2 diabetes that aim to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels. However, there are some key differences between the two.
1. Scope: Bariatric surgery is a broader term that encompasses various surgical procedures aimed at weight loss, including gastric bypass, gastric sleeve, and gastric banding. Metabolic surgery, on the other hand, specifically refers to surgical procedures that primarily target metabolic changes to improve blood sugar control, regardless of weight loss.
2. Mechanism of action: Bariatric surgery primarily works by reducing the size of the stomach or rerouting the digestive tract, which results in reduced food intake or impaired nutrient absorption. Metabolic surgery, on the other hand, focuses on altering the hormonal and metabolic processes in the body to enhance insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
3. Eligibility criteria: Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35-39.9 with obesity-related health conditions. Metabolic surgery, on the other hand, may be considered for individuals with a lower BMI (30-34.9) who have poorly controlled type 2 diabetes despite optimal medical management.
4. Weight loss outcomes: Bariatric surgery is primarily performed to achieve significant and sustained weight loss. Metabolic surgery, although it may result in some weight loss, primarily aims to improve blood sugar control and metabolic parameters.
5. Long-term effects: Both metabolic surgery and bariatric surgery have shown significant long-term benefits in terms of improved blood sugar control, reduced need for diabetes medications, and even remission of type 2 diabetes in some cases. However, the long-term effects on weight loss and overall health outcomes may differ between the two.
It’s important to note that the specific choice of surgical procedure should be based on a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, taking into consideration individual factors such as overall health, weight status, and diabetes management goals.
Last Words from the More Clinics
Surgical treatment for type 2 diabetes is a promising option for those who have not had success with traditional treatment methods. It can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels, weight loss, and overall health. However, it is important to discuss the risks and potential complications with your doctor and carefully consider if it is the right option for you. With the right approach and commitment to lifestyle changes, metabolic surgery can be an effective tool in managing type 2 diabetes.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION!
Let’s Start Planning Your Treatment %100 Guarantee Results.